What Goes into a Credit Score?
Your credit score is made up of five factors that creditors look at to determine your level of risk. Each element has a different weight towards your credit score.*
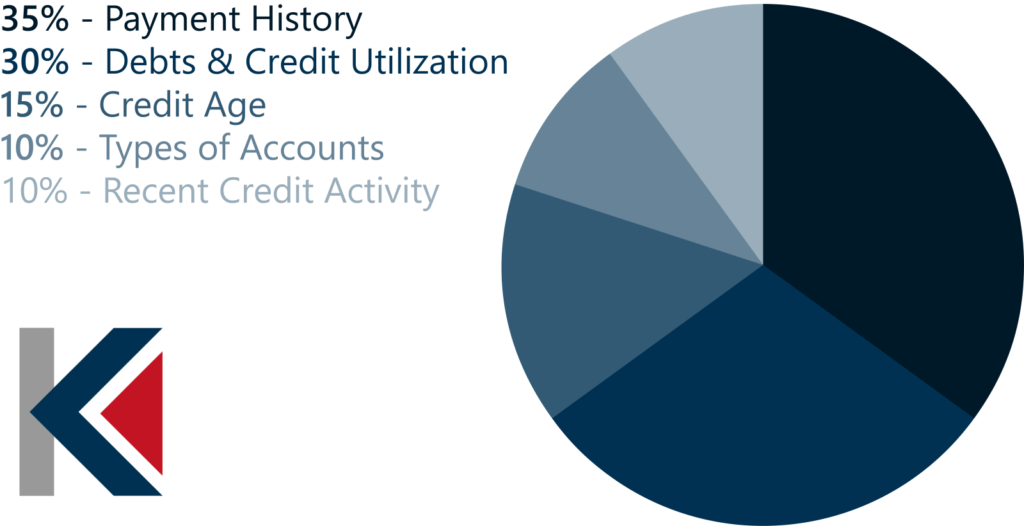
- Payment History – 35%
Your record of payments to your credit card bill and other debts is considered when factoring in your credit score. Having more late or missed payments will impact your score negatively. You can bring it back up by getting your payments back on track consistently over time.
- Debts and Credit Utilization – 30%
Having more debt makes you seem like a “riskier” option in the eyes of creditors. Keeping your credit utilization rate under 30% is a good way to maintain a healthy credit score. You can do so by setting balance alerts and making extra payments during the month.
- Credit Age – 15%
The longer you’ve been using credit, the better your credit score can be.
- Types of Accounts – 10%
How many and what types of credit accounts you have will impact your credit score. This goes beyond just credit cards and includes mortgages, car loans, student loans, etc.
- Recent Credit Activity – 10%
How frequently you have applied for credit impacts your credit score. It is important to minimize hard inquiries on your credit score when possible. Trying to apply for a new credit card, a car, a mortgage, and a personal loan in a short period of time makes you appear like a risky bet for creditors and will negatively impact your score.
What’s the Benefit of Having a High Credit Score?
A higher credit score can open doors for additional financial benefits and perks like the below:
- Lower interest rates on credit cards and loans
- Better chance for credit card and loan approval
- More negotiating power on financing
- Better car insurance rates
- Easier approval for rental properties
How Are Credit Scores Broken Down?
There are three credit bureaus that calculate credit scores: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. Technically, everyone has three credit scores. When a mortgage lender, for example, runs your credit, they consider the lower of the three scores to determine your creditworthiness.
Credit scores are categorized into five ranges:
- Exceptional: 800 – 850
- Very Good: 740 – 799
- Good: 670 – 739
- Fair: 580 – 669
- Poor: 300 – 579
How Can I Build My Credit Score?
Everyone starts somewhere. It takes time and consistency to build good credit. You can improve your credit score by:
- Paying your bills on time
- Using no more than 30% of your credit limit
- Keeping your accounts open and active
- Avoiding opening too many new accounts at once
- Checking your credit reports to dispute any errors
*Percentages from FICO via https://www.myfico.com/credit-education/whats-in-your-credit-score.






